Automatic Saree Border Weft Insertion
About the Practice
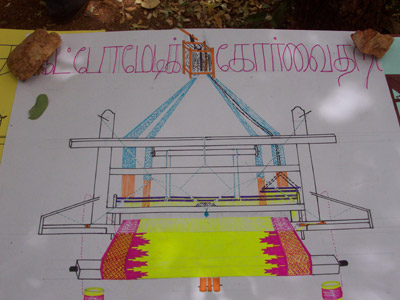
Traditionally, all the weavers in his village had the knowledge of weaving in sets only and not korvai loom weaving. Korvai or ?contrast? weaving involves intricate weaving where the design and often the colour of the borders are different from that on the main body of the cloth. Three shuttles are needed: weaver operates two having an assistant on third. While Banumurthi was happy receiving orders from Chennai and supplying new designs and varieties in clothes, he still fiddled with ways to improve productivity by using the loom effectively. He wanted to incorporate automatic koravi border insertion so that requirement of an assistant can be eliminated. He worked for a couple of months and in 1985 came up with his automated version on which only simple koravi weaving was possible.His restless mind did not seek peace with this success and he went on to make a fully automatic korvai loom in 1992, after a dedicated work of three months. This machine enabled him to do body weaving and border weaving uniformly apart from giving him the flexibility to weave borders ranging from 1? to 15? in width. Besides, as in modified handloom ?korvai looms?, rakes of all types (Thazampu rake, Sheet rake, Pillaiyar- moku) can be woven on his machine.
Detail:
His automated system is somewhat similar based to the Catch Cord Technique drawing device for looms. (United States Patent 4616680, 1984) though he was not aware of it. No assistant is In this technique. Multi Catch Cords are used to make Temple Borders. The number of catch cords is equal to the number of steps required in the Temple borders. Each step in the Temple Border is controlled by a separate Catch Cord and is individually operated by Dobby or Jacquard. In this technique, the picks per inch and the weave in temple border and the body of the sari are equal. This technique does not employ the. Three/two cut shuttle. style and thereby eliminates an additional manpower requirement. The steps of temple border are formed automatically by the operation of catch compared to the traditional three cut shuttle weaving. Bhanumurthi has installed one such device in Ramanathpuram village of Madurai district and trained about fifteen women weavers with the help of SEVA. A couple of years ago there were about 300 families involved in handloom weaving in this village but due to the inadequate income, about200 families migrated to nearby Tirupur Banian (vest) Factory for labour. After the installation of this device, response from people has been very good and they are hopeful that those who left the village would be willing to return and take up again, their traditional occupation. Indian Institute of Handloom Technology has commended this technique and suggested that it may be well adopted in handloom clusters, where Temple Borders are produced. GIAN Cell (Karnataka) is planning to conduct a training programme for handloom weavers in Karnataka region under Technical Education Quality Improvement Programme (TEQIP) of SSIT, Tumkur. Banumurthi was earlier felicitated with the SRISTI samman in 2006 for his innovation and contributions to the weaving society. Other Innovation Shivraj Multipurpose Equipment Motek Treadle Press: rejuvenating old letter printing press
About the Innovator
Address: Thiruvannamalai, Tamil Nadu
City: Thiruvannamalai
State: Tamil Nadu
PIN Code 606601
Practice Details
Link: This machine enabled him to do body weaving and border weaving uniformly apart from giving him the flexibility to weave borders ranging from 1 to 15 in width.
Manufacturing Capacity: d) Licensing, e) Franchising
Photo Links:
News Link 5: